VLAN Configuration on GajShield Firewall
Definitions:
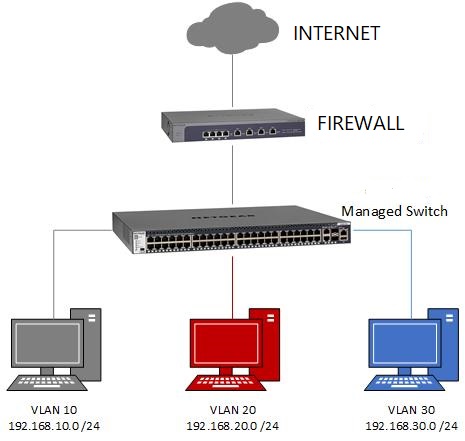
A Virtual LAN (VLAN) is any broadcast domain that is partitioned and isolated in a computer network at the data link layer (OSI layer 2). VLANs work by applying tags to network frames and handling these tags in networking systems - creating the appearance and functionality of network traffic that is physically on a single network but acts as if it is split between separate networks. In this way, VLANs can keep network applications separate despite being connected to the same physical network, and without requiring multiple sets of cabling and networking devices to be deployed. VLANs allow network administrators to group hosts together even if the hosts are not directly connected to the same network switch. Because VLAN membership can be configured through software, this can greatly simplify network design and deployment. Without VLANs, grouping hosts according to their resource needs the labor of relocating nodes or rewiring data links. VLANs allow devices that must be kept separate to share the cabling of a physical network and yet be prevented from directly interacting with one another. This managed sharing yields gains in simplicity, security, traffic management, and economy. For example, a VLAN can be used to separate traffic within a business based on individual users or groups of users or their roles (e.g. network administrators), or based on traffic characteristics (e.g. low-priority traffic prevented from impinging on the rest of the network's functioning). To subdivide a network into VLANs, one configures network equipment. Simpler equipment might partition only each physical port (if even that), in which case each VLAN runs over a dedicated network cable. More sophisticated devices can mark frames through VLAN tagging, so that a single interconnect (trunk) may be used to transport data for multiple VLANs. Since VLANs share bandwidth, a VLAN trunk can use link aggregation, quality-of-service prioritization, or both to route data efficiently.
VLAN Network configured on L3 Switch:
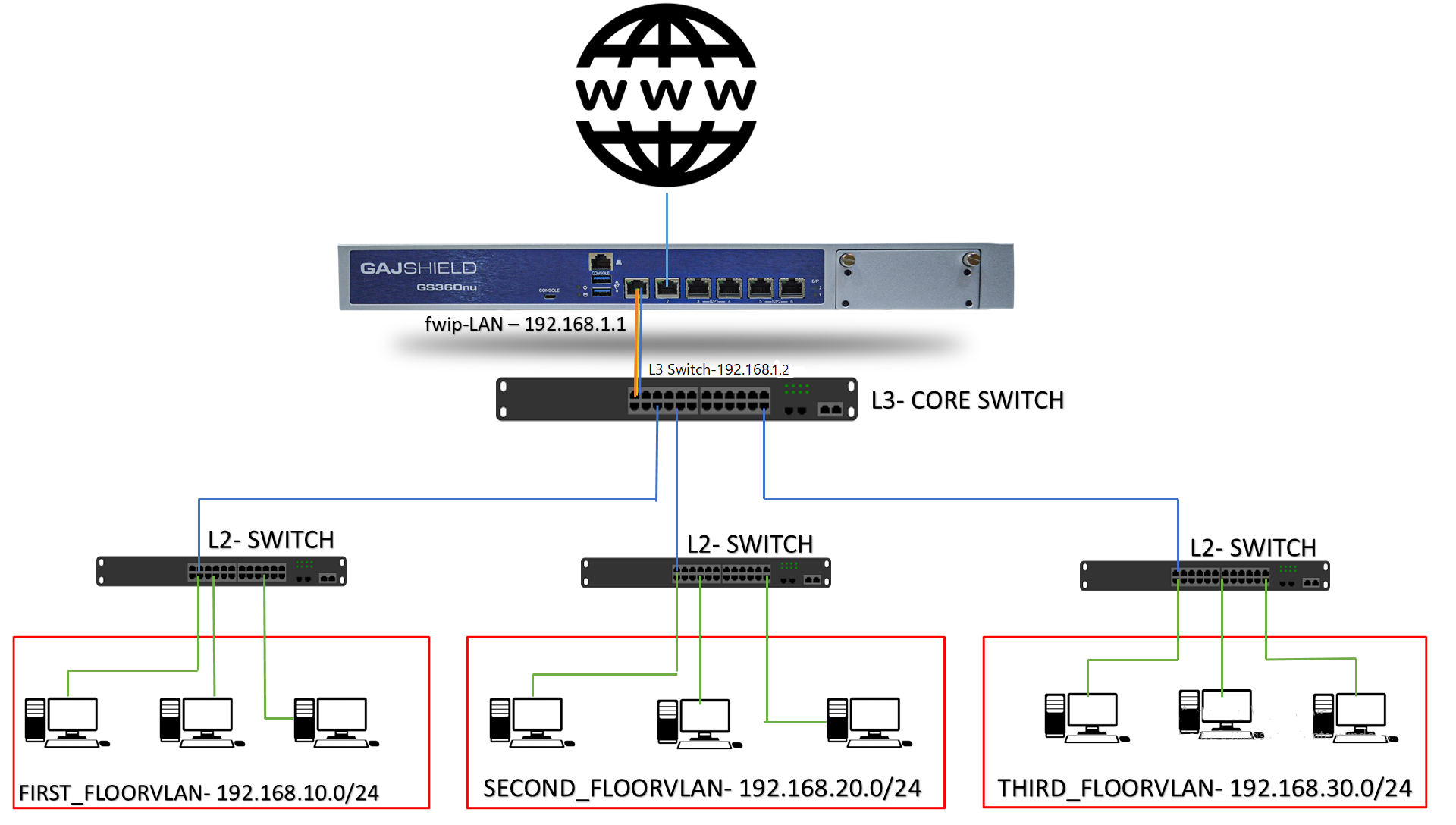
Routes and tagging is done in L3 switch
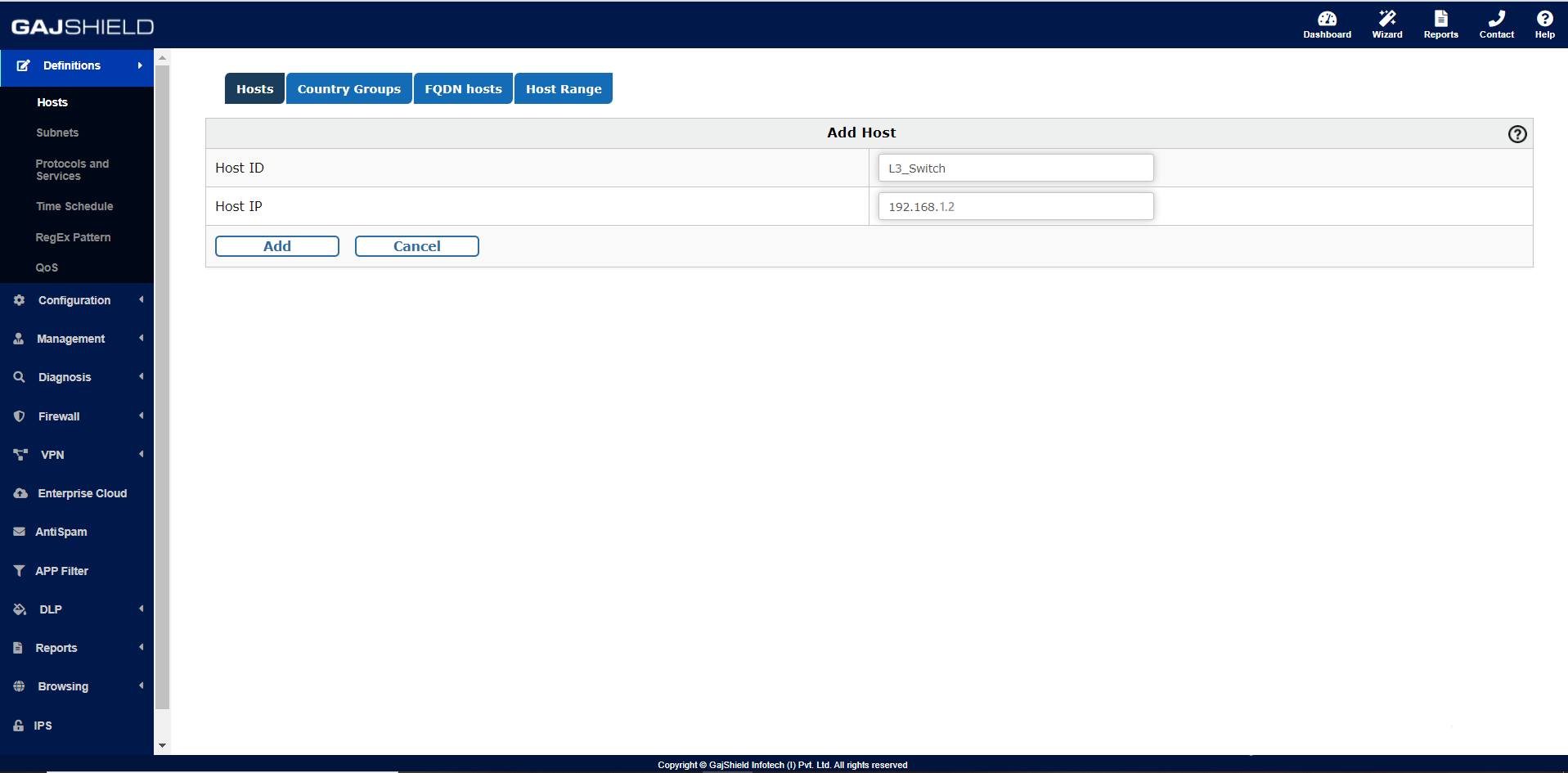
Similarly we need to create a Host entry of the L3-switch IP. For that you need to go on,
Definition >> Hosts >> Hosts >> +,
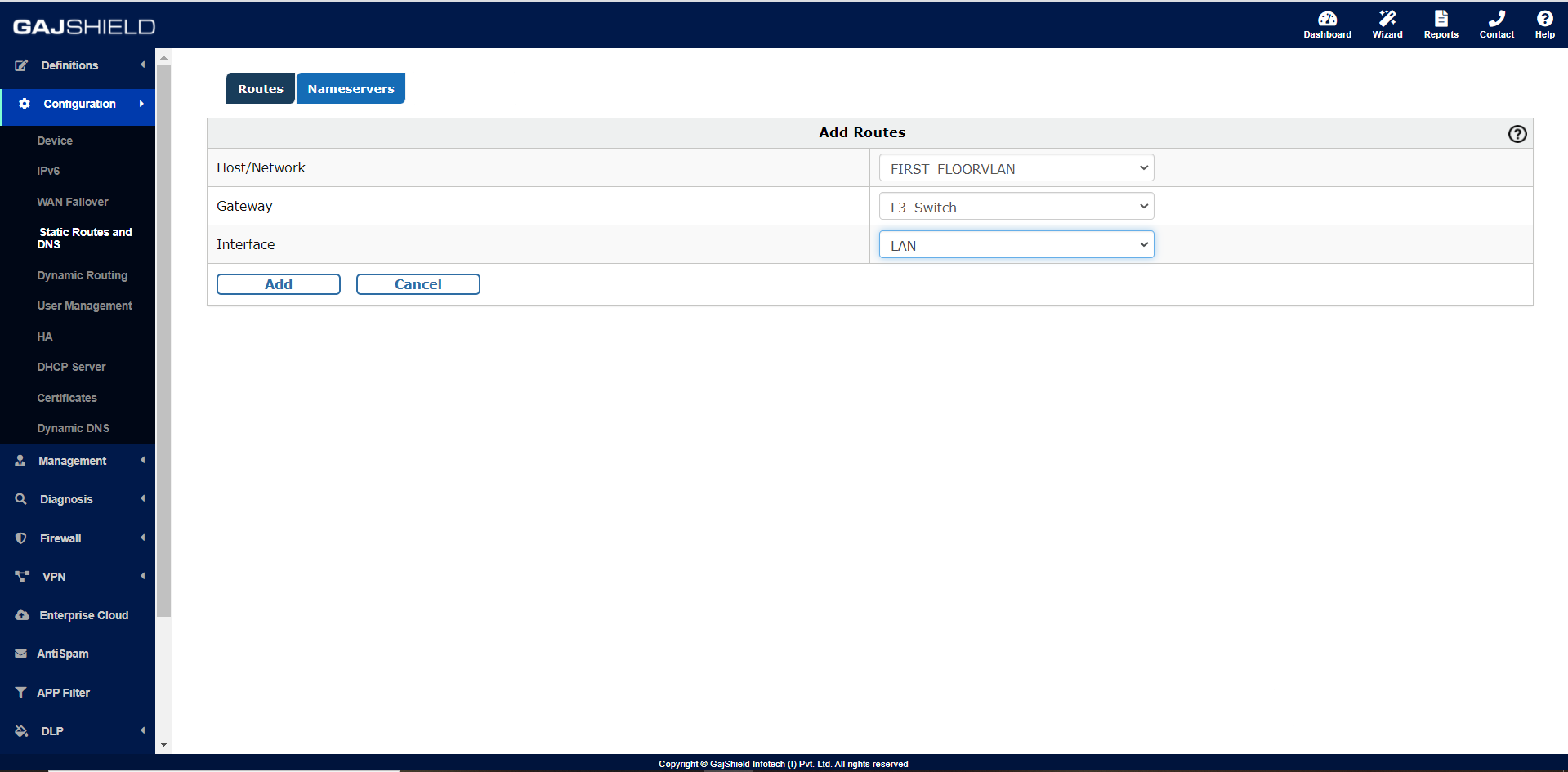
To configure the Static routes on the firewall by going to
Configuration >> Static Routes and DNS >> Routes >> +,
Version- IPv4
Host/Network = Created VLAN Network (FIRST_FLOORVLAN)
Gateway = L3-Switch (Host IP- 192.168.1.2)
Interface = LAN
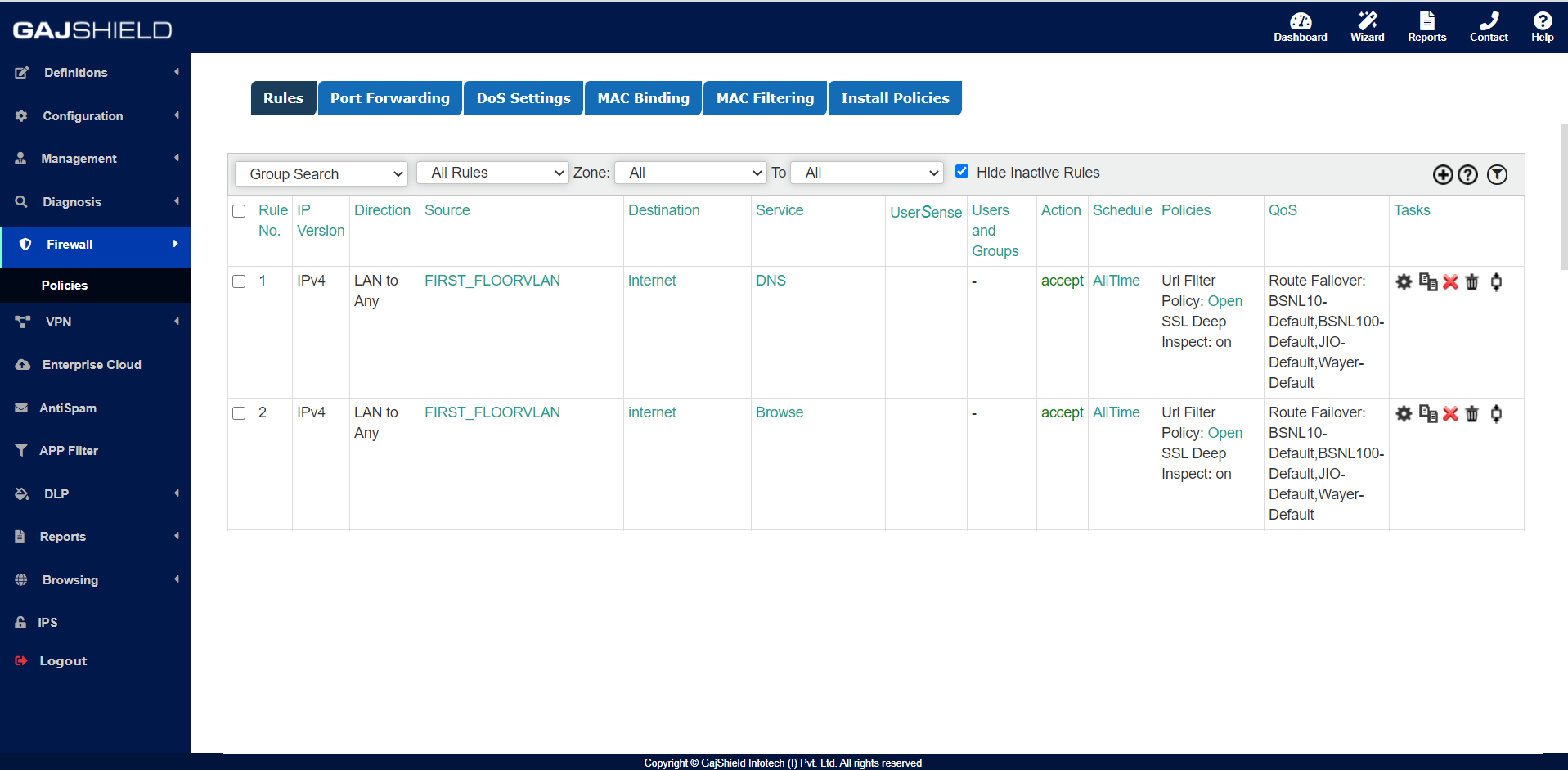
Firewall Rule:
Direction: LAN TO ANY
Source: FIRST_FLOORVLAN
Destination: Internet
Service: DNS, Browse
URL POLICY
LINK ROUTE FAILOVER
>> Install Policy
Logs:
2020:12:10-11:47:38 kernel: [10182931.458168] GSHIELD=pass*rule-1 IN=eth0 OUT=eth4 MAC=00:02:b6:45:d6:0b:00:ad:24:eb:06:83:08:00 SRC=192.168.10.99 DST=8.8.8.8 LEN=52 TOS=0x00 PREC=0x00 TTL=126 ID=48454 DF PROTO=UDP SPT=52561 DPT=53 WINDOW=64240 RES=0x00 SYN URGP=0 MARK=0x5
2020:12:10-11:47:39 kernel: [10182931.458168] GSHIELD=pass*rule-2 IN=eth0 OUT=eth4 MAC=00:02:b6:45:d6:0b:00:ad:24:eb:06:83:08:00 SRC=192.168.10.99 DST=104.254.149.100 LEN=52 TOS=0x00 PREC=0x00 TTL=126 ID=48454 DF PROTO=TCP SPT=52561 DPT=443 WINDOW=64240 RES=0x00 SYN URGP=0 MARK=0x5
VLAN interface configured on firewall:
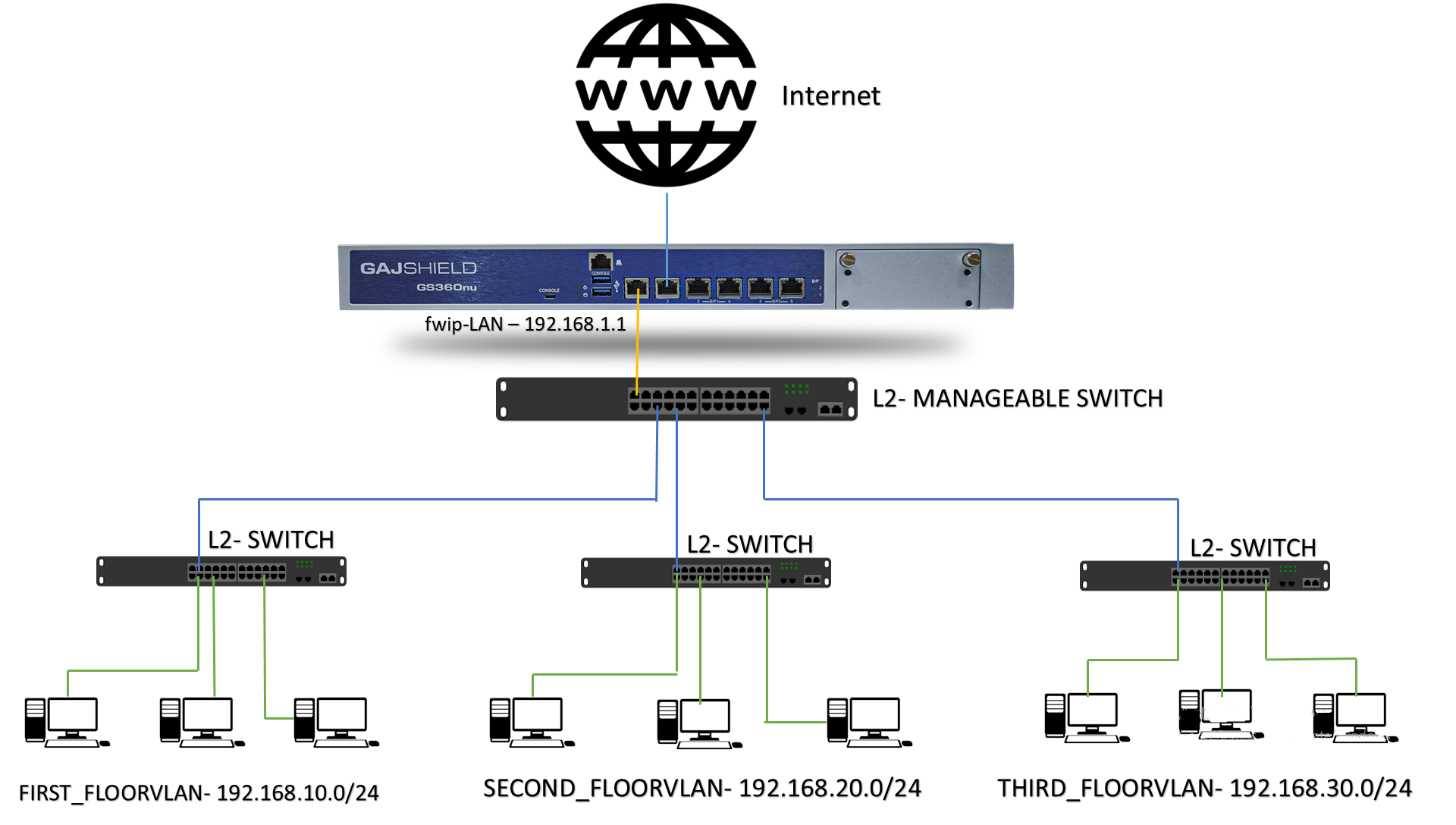
All the configuration is done on the firewall
First step is to configure management interface (it could be any interface of firewall) on which you have to configure the VLAN interfaces. So in the above diagram we have configured the VLAN on Interface 01 of the firewall.
L3 switch Trunk port:
A trunk port allows you to send all those signals for each switch/router/firewall across a single trunk link. In contrast to an access port, a trunk port must use tagging in order to allow signals to get to the correct endpoint. Trunk ports typically offer higher bandwidth and lower latency than access ports.
VLAN ID:
A VLAN represents a broadcast domain. VLANs are identified by a VLAN ID (a number between 0 – 4095), with the default VLAN on any network being VLAN 1. Each port on a switch or router can be assigned to be a member of a VLAN (i.e., to allow receiving and sending traffic on that VLAN).
When customer will be configuring the trunk port directly with the firewall. From the manageable switch every interface will be having a separate VLAN ID so we need to get the VLAN ID and need to configure the same on the firewall with its IP address so all the traffic routing will be managed from the firewall.
Then you need to create VLAN entry on the firewall, Configuration >> Device >> VLAN >> +,
VLAN Name: FIRST_FLOORVLAN
VLAN ID (Must be (2 - 4094)): 10
VLAN Interface: LAN
IPv4 Configuration:
IP Address: 192.168.20.0
Netmask: 255.255.255.0
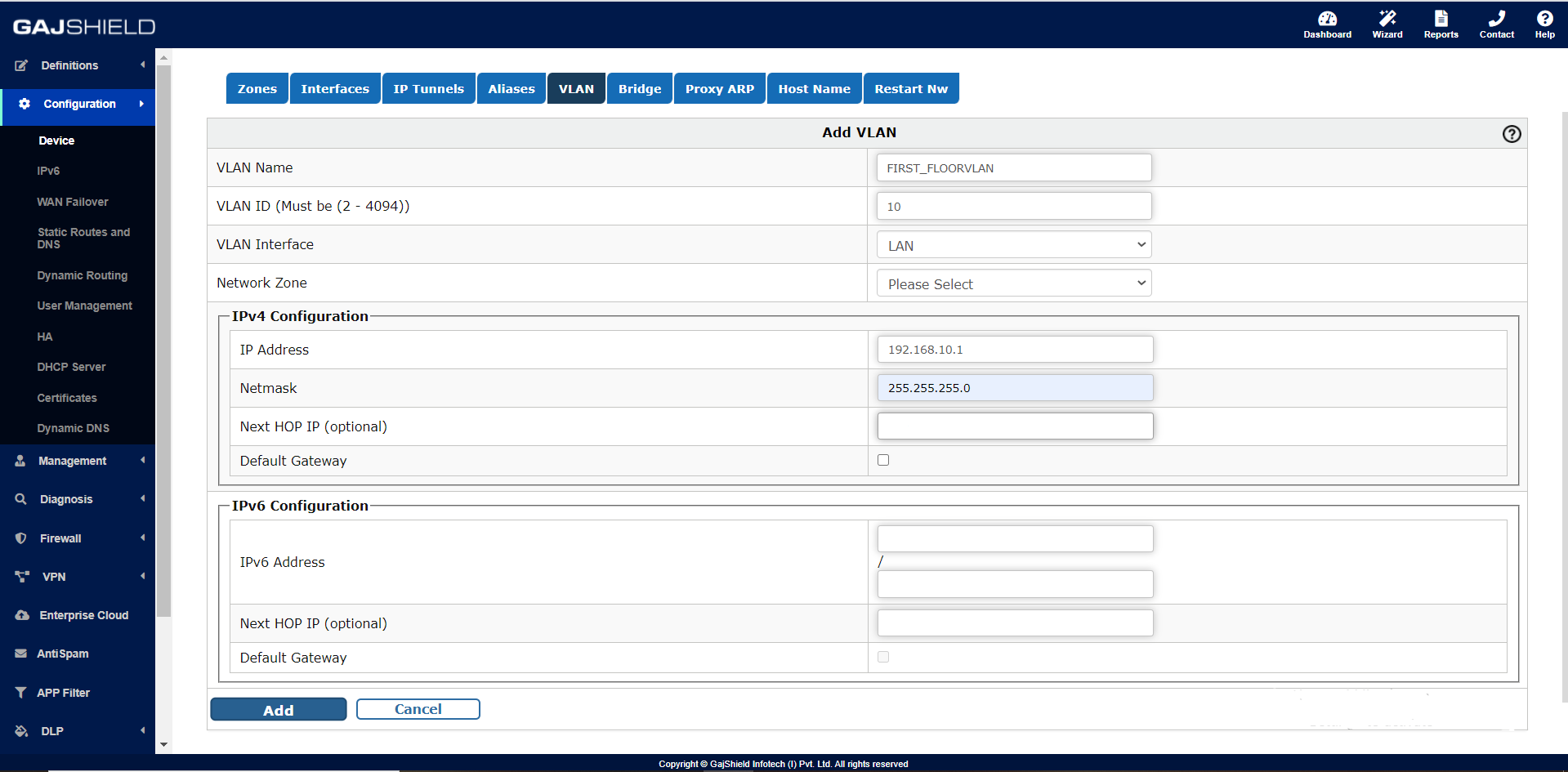
If you are configuring VLAN interface for ISP then next hope IP is required i.e. router IP and not firewall LAN or WAN interface IP.
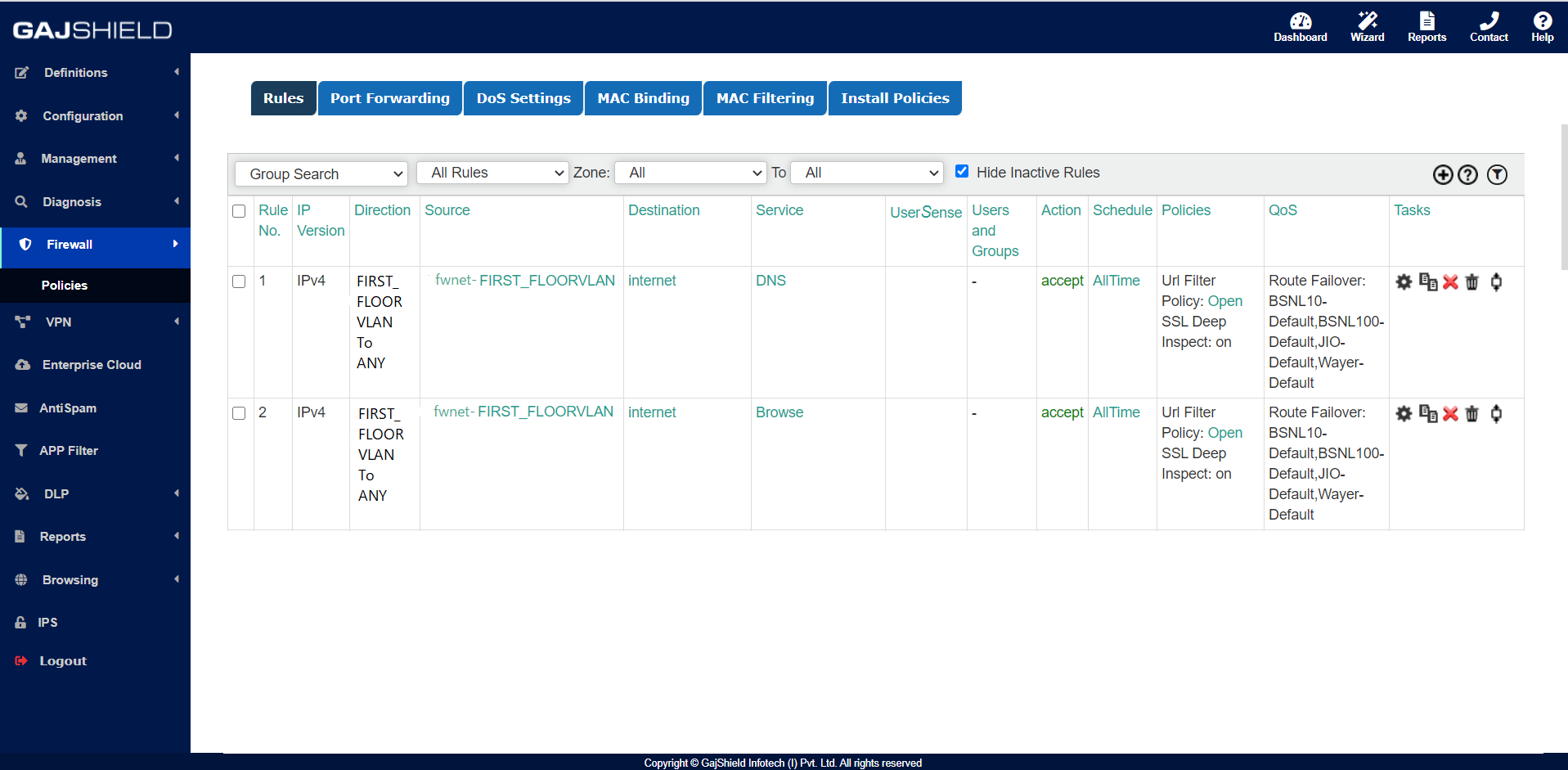
As soon as we will add the VLAN configuration automatically firewall will create a network on the firewall as fwnet-FIRST_FLOORVLAN.
Firewall Rule:
Direction: FIRST_FLOORVLAN TO ANY
Source: fwnet-FIRST_FLOORVLAN
Destination: Internet
Service: DNS, Browse
URL POLICY
LINK ROUTE FAILOVER
>> Install Policy
Logs:
2020:12:04-10:50:17 kernel: [11740735.366310] GSHIELD=pass*rule-2 C OUT=eth4 MAC=08:35:71:f2:9d:3b:68:f7:28:5d:f1:9d:08:00 SRC=192.168.10.69 DST=142.250.67.37 LEN=52 TOS=0x00 PREC=0x00 TTL=127 ID=17402 DF PROTO=TCP SPT=56260 DPT=443 WINDOW=64240 RES=0x00 SYN URGP=0 MARK=0x28 USR=0 GRP=0 DEV=0 APP=1635
2020:12:04-10:50:17 kernel: [11740735.378850] GSHIELD=pass*rule-1 IN=eth0.10 OUT=eth1 MAC=08:35:71:f2:9d:3b:c6:a7:99:a6:35:77:08:00 SRC=192.168.10.69 DST=8.8.8.8 LEN=60 TOS=0x00 PREC=0x00 TTL=63 ID=60547 DF PROTO=UDP SPT=42599 DPT=53 WINDOW=65535 RES=0x00 SYN URGP=0 MARK=0x2a USR=0 GRP=0 DEV=0 APP=1635
2020:12:04-10:50:18 kernel: [11740736.065446] GSHIELD=pass*rule-93 IN=eth0.27 OUT=eth1 MAC=08:35:71:f2:9d:3b:00:1b:09:06:18:98:08:00 SRC=10.0.27.129 DST=14.141.16.21 LEN=60 TOS=0x00 PREC=0x00 TTL=63 ID=11058 DF PROTO=TCP SPT=51377 DPT=11000 WINDOW=5840 RES=0x00 SYN URGP=0 MARK=0x2a USR=0 GRP=0 DEV=0 APP=1635
2020:12:04-10:50:17 kernel: [11740735.378850] GSHIELD=pass*rule-14 IN=eth0.99 OUT=eth3 MAC=08:35:71:f2:9d:3b:c6:a7:99:a6:35:77:08:00 SRC=10.0.99.56 DST=74.125.158.234 LEN=60 TOS=0x00 PREC=0x00 TTL=63 ID=60547 DF PROTO=TCP SPT=42599 DPT=443 WINDOW=65535 RES=0x00 SYN URGP=0 MARK=0x2a USR=0 GRP=0 DEV=0 APP=1635
Note:
While configuring VLAN on the firewall, in firewalllog you will be getting the tag ID IN=eth0.10 i.e. it’s from the VLAN 10 = fwnet-FIRST_FLOORVLAN, that means the trunking, VLAN tagging and routing is managed from the firewall.
In L3 switch logs you will find basic logs, since all the traffic switching and management is done from the L3 core switch and the firewall is only applying the security policies and routing the traffic to internet. So there is no tag ID observed in the firewalllog’s.